In this article, we will look at how to implement dynamic routes in Vue application using the vue-router package.
We will begin by creating a new application using Vue CLI.
❯ vue create dynamic-routes-demo
Once, the installation is complete, we can navigate to the folder and run the server to load the application.
❯ cd dynamic-routes-demo
❯ npm run serve
This will run our server on port 8080 by default http://localhost:8080/
Next, we will install the vue-router package required for routing. We can install it using CDN, npm or yarn.
npm:
npm install vue-router@4
yarn:
yarn add vue-router@4
Once the package is installed, we can integrate it with our Vue application.
In this application, we will have a “products” page that will list all the products. Let’s create the component for the same.
// Terminal
❯ touch src/components/ProductList.vue
Let’s add some code to the ProductList.vue file.
<!-- ProductList.vue -->
<template>
<h1>Products</h1>
</template>
This component can now be imported into the main.js file.
// main.js
import { createApp } from "vue";
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from "vue-router";
import App from "./App.vue";
import ProductList from "./components/ProductList";
const app = createApp(App);
app.mount("#app");
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(),
routes: [
{
path: "/products",
component: ProductList,
},
],
});
app.use(router);
To display the component content, we need to add <router-view> component to the App.vue.
We will also declare the products in the provide() option so that they will be available for the other components.
<!-- App.vue -->
<template>
<router-link to="/products">Products</router-link>
<router-view></router-view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
provide() {
return {
products: [
{
id: 1,
name: "Apple Macbook Pro",
price: "$3000",
},
{
id: 2,
name: "Apple iPhone 12",
price: "$3000",
},
{
id: 3,
name: "Apple iPhone 13",
price: "$1000",
},
{
id: 4,
name: "Apple iPhone 14",
price: "$2000",
},
],
};
},
};
</script>
Let’s populate the products in the ProductList.vue
<!-- ProductList.vue -->
<template>
<h1>Products</h1>
<div>
<div v-for="product in products" :key="product.id">
<router-link :to="'/products/' + product.id">
{{ product.name }}
</router-link>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "ProductList",
inject: ["products"],
};
</script>
Notice, we are passing id in the <router-link> using single quotes.
<router-link :to="'/products/' + product.id">
The URL will change with the value of product.id, for example
/products/1
/products/2
/products/abc
/products/1323344
All the above paths are valid. Hence, we need a way to define the dynamic route. Let’s make changes in the main.js file to add this dynamic route.
{
path: "/products/:id",
component: TheProduct,
}
Here, the path property contains :id which indicates a dynamic route since the value of id is not fixed. You can name it anything you want but ensure that: is prefixed.
The entire main.js file will now contain the following code:
// main.js
import { createApp } from "vue";
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from "vue-router";
import App from "./App.vue";
import ProductList from "./components/ProductList";
import TheProduct from "./components/TheProduct";
const app = createApp(App);
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(),
routes: [
{
path: "/products",
component: ProductList,
},
{
path: "/products/:id",
component: TheProduct,
},
],
});
app.use(router);
app.mount("#app");
We have also declared a new component TheProduct for the dynamic route. Let’s create the component file and add the code.
<!-- TheProduct.vue -->
<template>
<h1>{{ product.name }}</h1>
<h2>{{ product.price }}</h2>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "TheProduct",
inject: ["products"],
data() {
return {
product: {},
};
},
created() {
const id = this.$route.params.id;
this.product = this.products.find((product) => product.id == id);
},
};
</script>
In this component, we will display the name and the price of the product.
We are making use of the $route.params which gives us the parameters present in the URL. In our case, we have one parameter id.
const id = this.$route.params.id;
To fetch the product, we are making use of the find method to search the product by id value and display it.
this.product = this.products.find((product) => product.id == id);
Let’s look at the output:
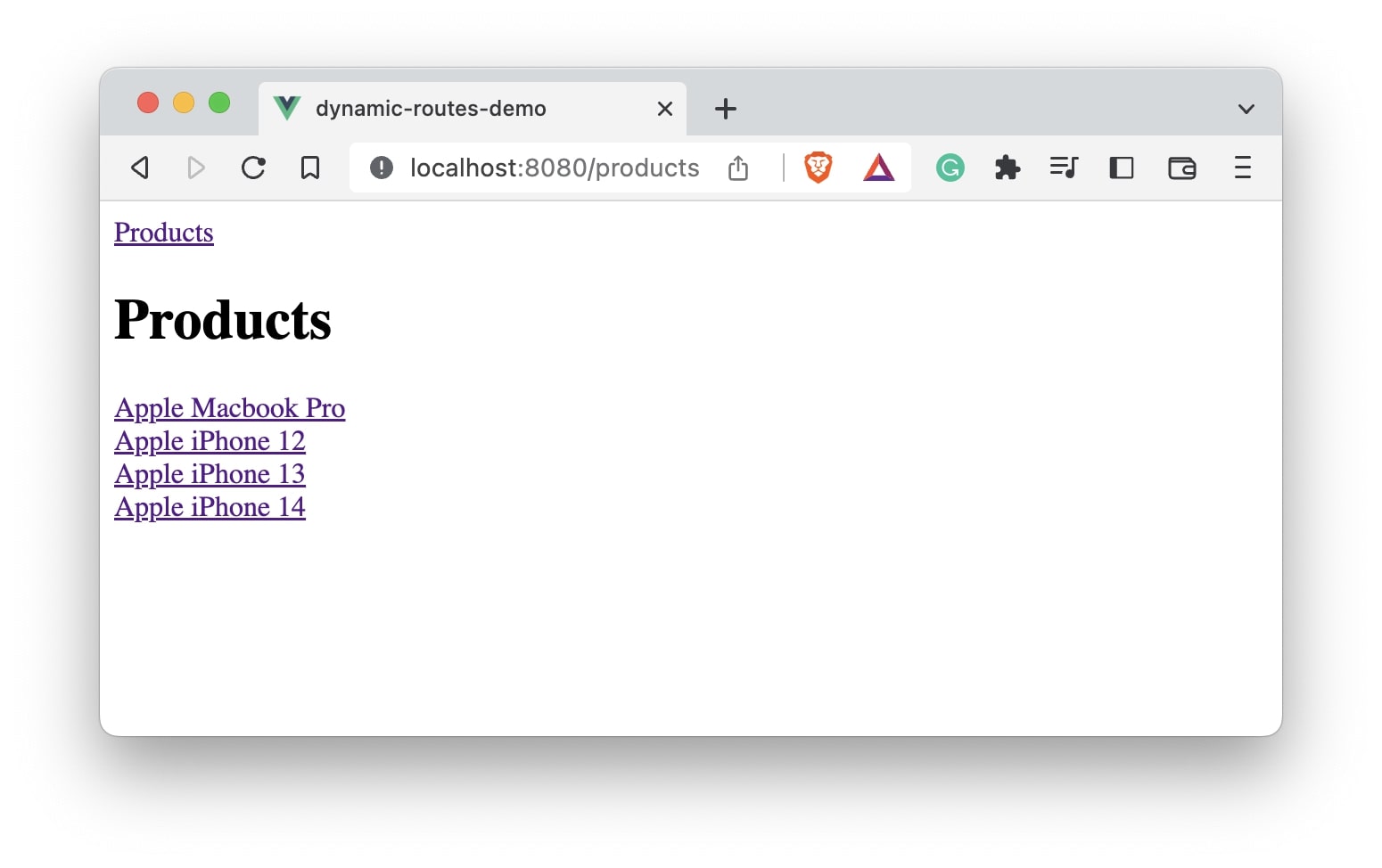
We have /products page which display all the products available. Let’s click the link of the first product to see what happens.
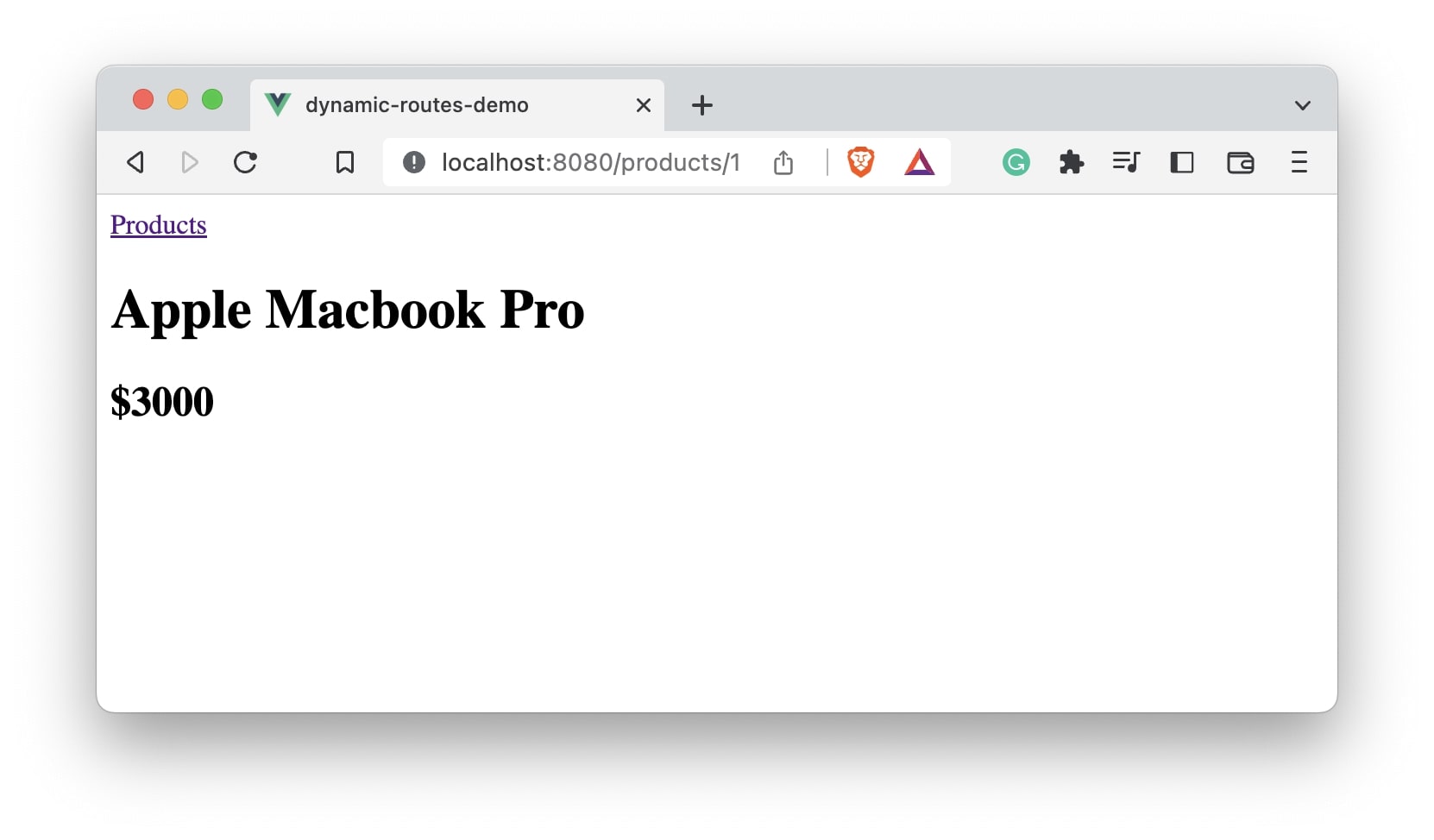
I have clicked the first link and the page with URL /products/1 gets opened. As expected, the product name and price gets displayed.
Let’s go back and click the second link.
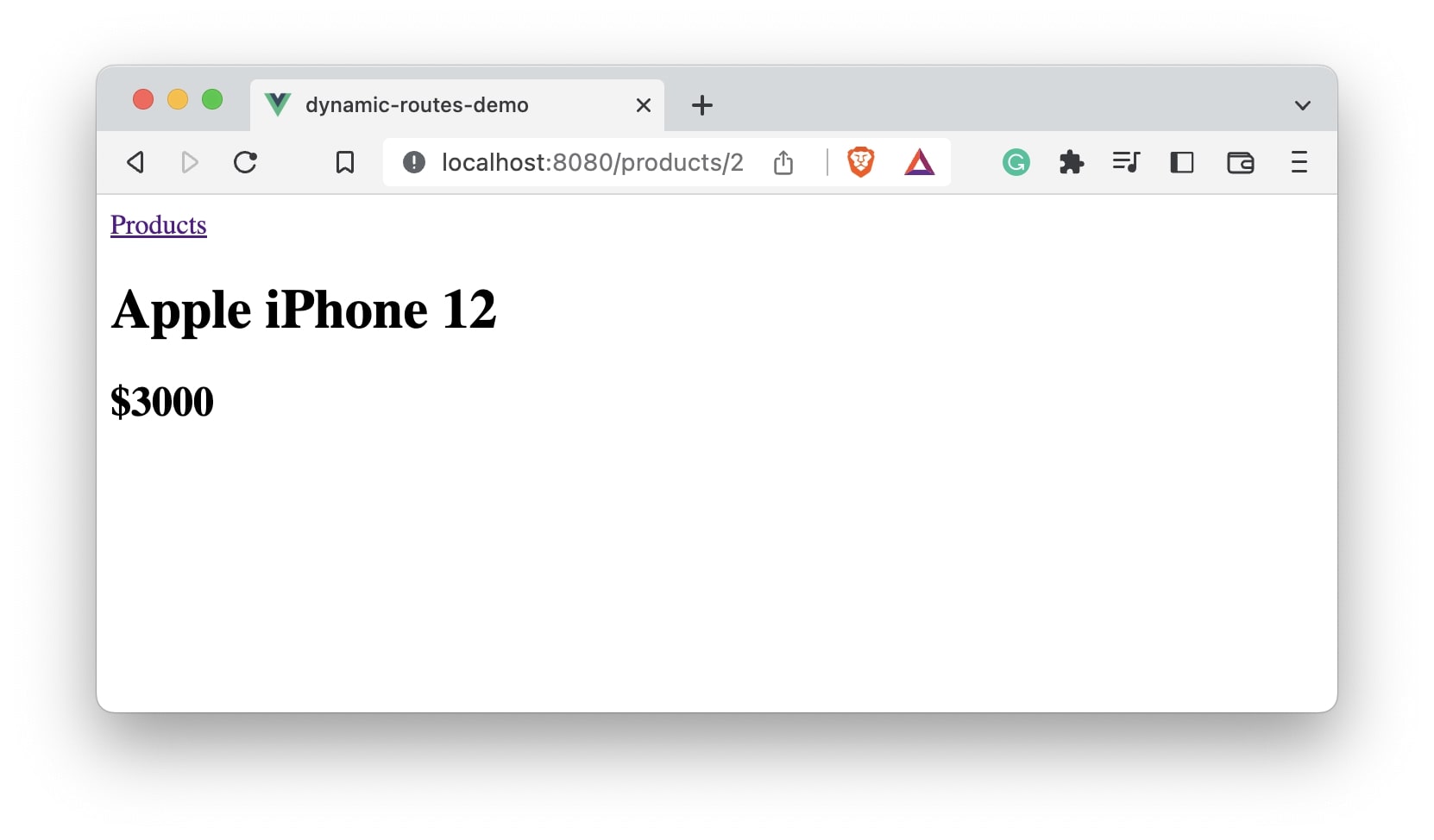
As you can see, /products/2 link gets opened with a different product details. This way you can implement dynamic routes in Vue application.