Table of Contents
- Introduction
- v-if
- v-else
- Using v-if on template
- v-else-if Multiple conditions
- Difference between v-if and v-show
Introduction
To conditionally render the block, Vue uses the v-if directive. In this article, we will look at how to use v-if directive in Vue with examples.
v-if
<span v-if="true">Hey there!</span>
If the expression assigned to v-if returns a truthy value, the block gets rendered in DOM.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Conditional vue</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p v-if="lorem">
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod
tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
</p>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
lorem: true
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
In the above example, if the value of ‘lorem’ is set to false, the <p> will not be rendered.
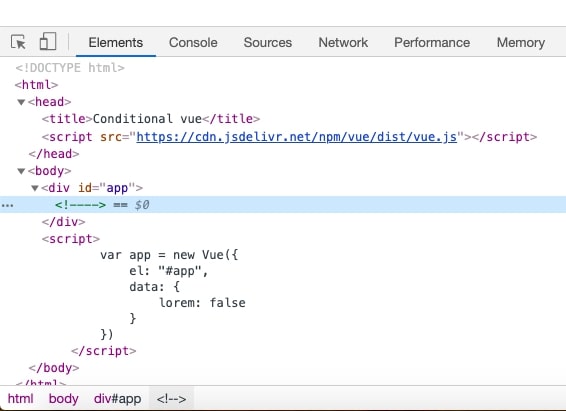
v-else
Vue also provides us with v-else directive which renders the block if v-if expression returns false. Remember v-else should also be declared immediately after v-if.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Conditional vue</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<span v-if="textCheck">v-if is false</span>
<span v-else>Rendered using v-else</span>
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
textCheck: false
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
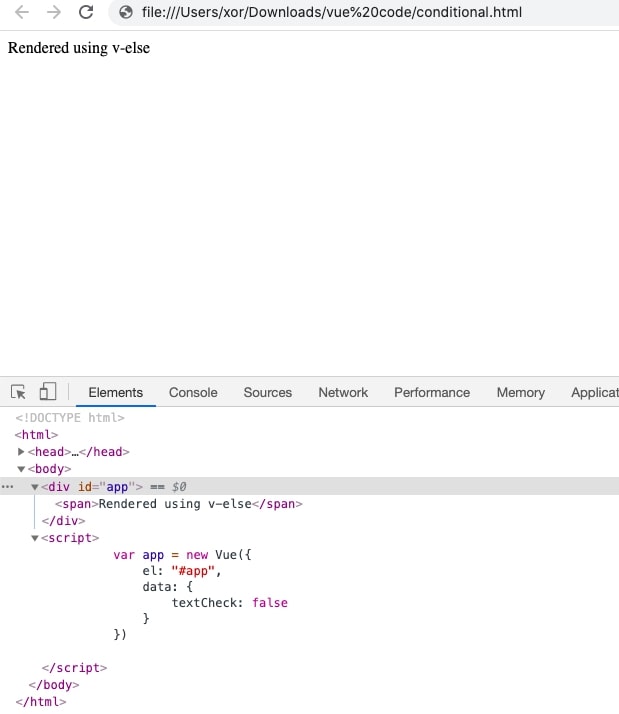
Using v-if on template
You can also use v-if on a template to apply condition on group of elements.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Vue if/else</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<template v-if="display">
<div>
<h1>Hello</h1>
<p>Paragraph 1</p>
<p>Paragraph 2</p>
</div>
</template>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
display: true
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
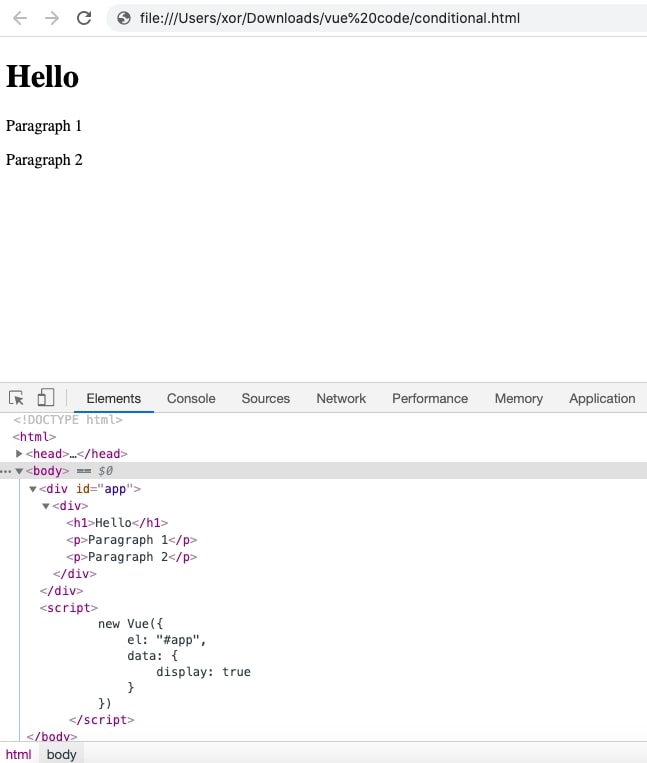
When the condition is false:
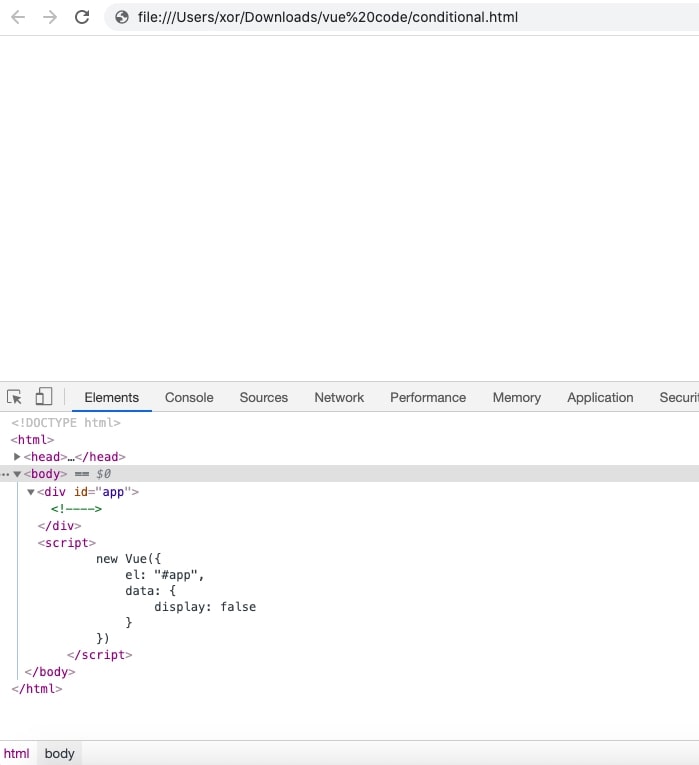
v-else-if Multiple conditions
From version 2.1.0+ we can define “else if” block. You can use one or more v-else-if directives to handle multiple conditions.
<div id="app">
<h1 v-if="display === 1">1</h1>
<h1 v-else-if="display === 2">2</h1>
<h1 v-else-if="display === 3">3</h1>
<h1 v-else-if="display === 4">4</h1>
<h1 v-else-if="display === 5">5</h1>
<h1 v-else>6</h1>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
display: 6
}
})
</script>
Difference between v-if and v-show
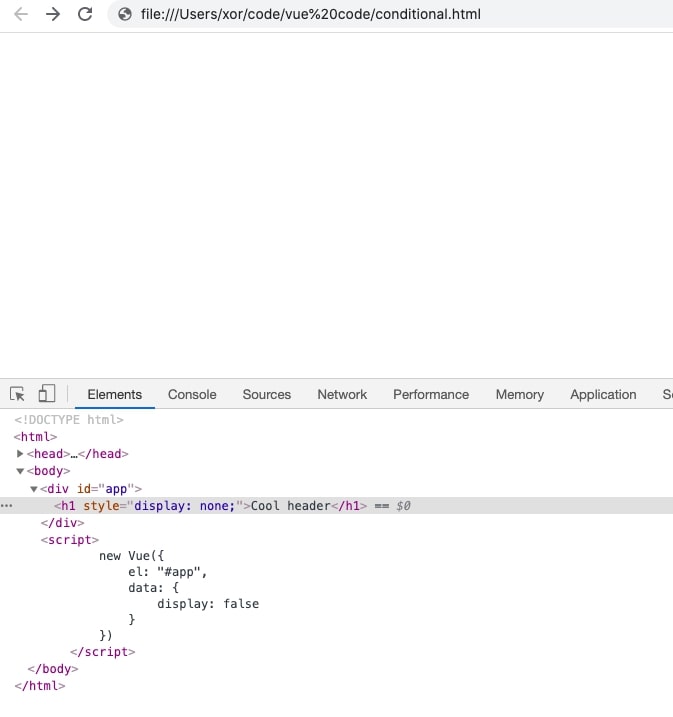
Both v-if and v-show are different from each other in the way they work. The v-show directive uses the CSS property ‘display’ to show or hide the content whereas, v-if directive renders the content in the DOM if the expression is evaluated to true. If the expression of v-if results in false the content is not rendered in DOM.
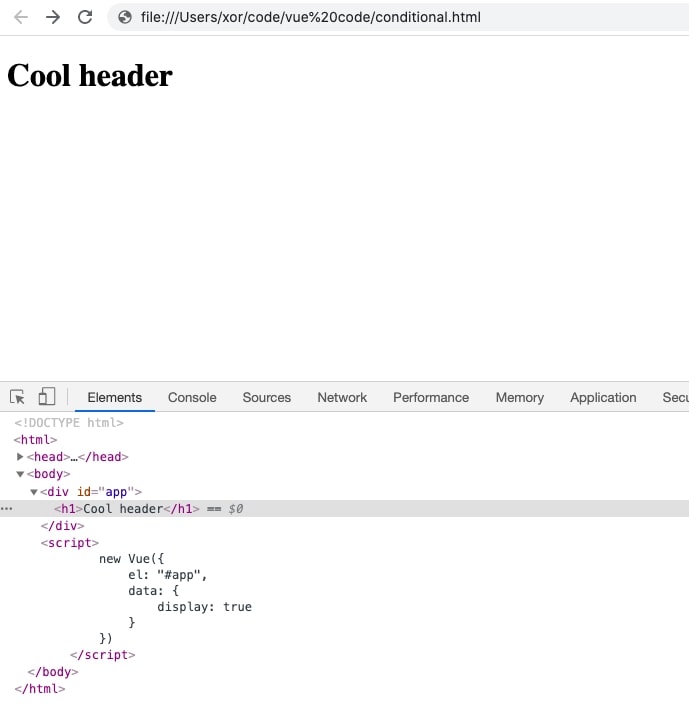
v-show
<div id="app">
<h1 v-show="display">Cool header</h1>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
display: true
}
})
</script>
<div id="app">
<h1 v-show="display">Cool header</h1>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
display: false
}
})
</script>
v-if
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Conditional vue</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<h1 v-if="display">Cool header</h1>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
display: false
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

Choosing between v-if and v-show
If you need to perform one or the other operation depending on the expression value, use v-if. That is if you need to use v-else if the v-if evaluates to false it makes sense in such a scenario to use v-if. For example, if the user is signed in, display a logout button or else display a login button.
The v-show directive simply displays or hides the element using CSS property. Think of a scenario where you might use a “display: none” property, use v-show instead. For example, hide a task from the listed if it is completed.