There are two ways of registering components in Vue.
- Globally
- Locally
In this article, we will look at how to declare and use components both locally and globally.
We will start by creating an application using Vue CLI.
❯ vue create local-global-demo
Once, the installation is complete, we can navigate to the folder and run the server to load the application.
❯ cd local-global-demo
❯ npm run serve
This is run the server on port 8080 http://localhost:8080/
Global Components
When you declare a component globally, it will be available throughout the application. We usually declare global components in the main.js file.
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
createApp(App).mount('#app')
Let’s make some changes in the main.js file so that we can declare global components.
import { createApp } from "vue";
import App from "./App.vue";
const app = createApp(App);
app.mount("#app");
We declare a constant app and assign the createApp function.
To declare a component in this file, we need to first create one. Let’s create a new component file within the /src/components folder.
❯ touch src/components/MyComponent.vue
Let’s open the file and add some code.
<template>
<h2>My Component</h2>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "MyComponent",
};
</script>
Next, we will register this component. in the main.js file.
First, we will need to import the component into the main.js.
// main.js
import MyComponent from "./components/MyComponent.vue";
The component can then be declared using app.component().
app.component("MyComponent", MyComponent);
The first argument is the component name and the second argument is the implementation of the component.
The complete main.js file now contains the below code:
import { createApp } from "vue";
import App from "./App.vue";
import MyComponent from "./components/MyComponent.vue";
const app = createApp(App);
app.mount("#app");
app.component("MyComponent", MyComponent);
Now, we can easily use the component MyComponent in any other component file directly.
For example, let’s use this component in the App.vue.
// App.vue
<template>
<MyComponent />
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
};
</script>
The <MyComponent /> is now available to be used in the App.vue file or any other components.
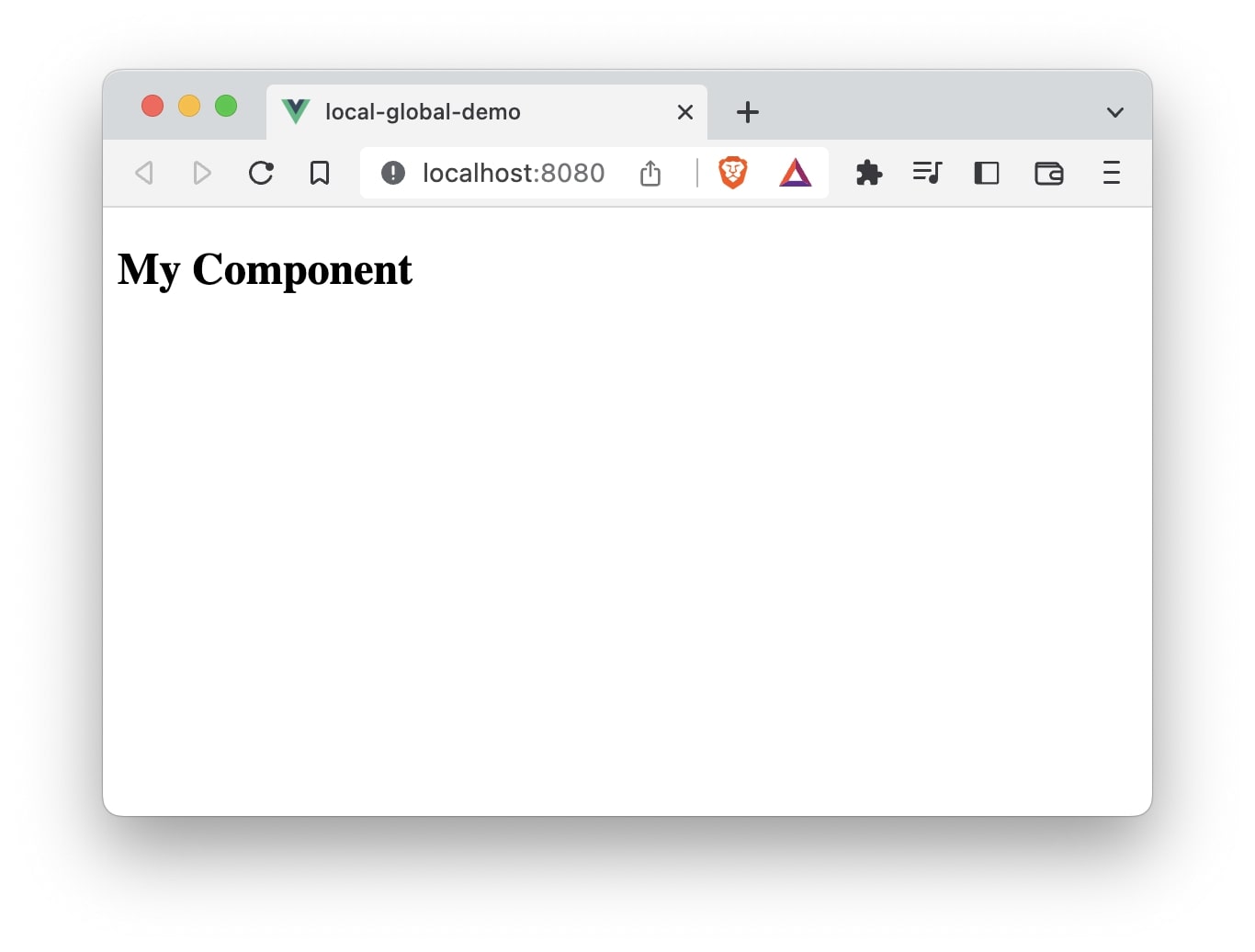
If there are multiple components that need to be declared globally, use add them in the main.js file like below:
// main.js
import MyComponent from "./components/MyComponent.vue";
import FirstComponent from "./components/FirstComponent.vue";
import SecondComponent from "./components/SecondComponent.vue";
import ThirdComponent from "./components/MyComponent.vue";
app.component("MyComponent", MyComponent);
app.component("FirstComponent", MyComponent);
app.component("SecondComponent", MyComponent);
app.component("ThirdComponent", MyComponent);
Local Components
Local components are only available in the components they are registered in.
To see it in action, let’s register a local component called LocalComponent in the App component.
We will first create a component file - LocalComponent.vue.
❯ touch src/components/LocalComponent.vue
We will add some code in this file in order to test it.
<template>
<h2>I am included as Local Component in App</h2>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "LocalComponent",
};
</script>
In the App.vue file we will import the newly created file and also declare it using components option.
<template>
<MyComponent />
<LocalComponent />
</template>
<script>
import LocalComponent from "./components/LocalComponent.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
LocalComponent,
},
};
</script>
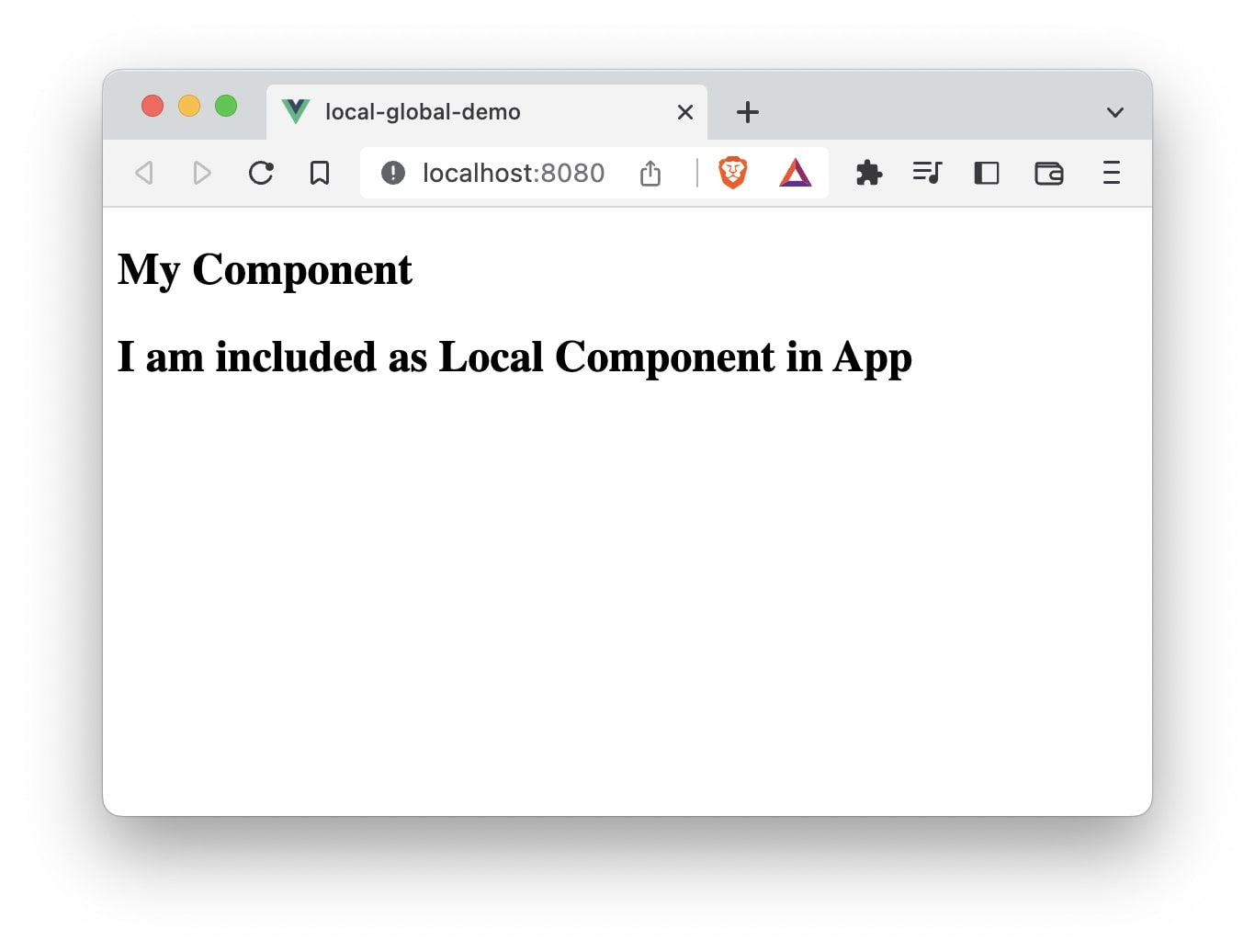
It is important to note that LocalComponent is only available to be used in App component. If you want to use it in any other component, you will have to register it in the component that wants to use it.